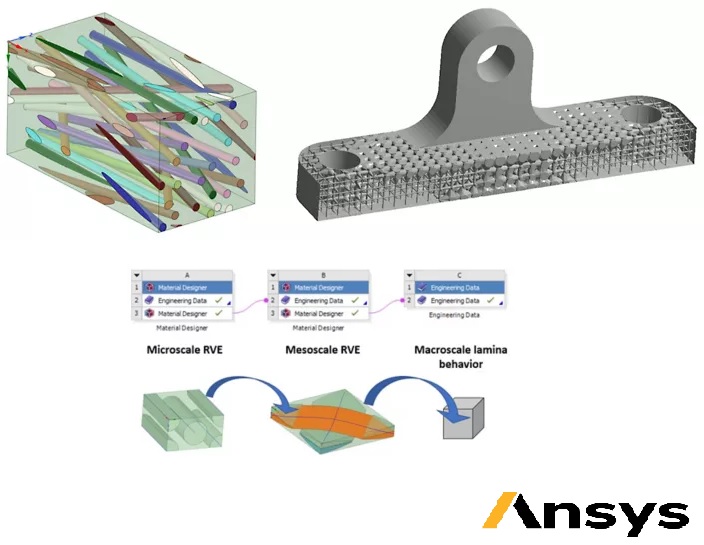
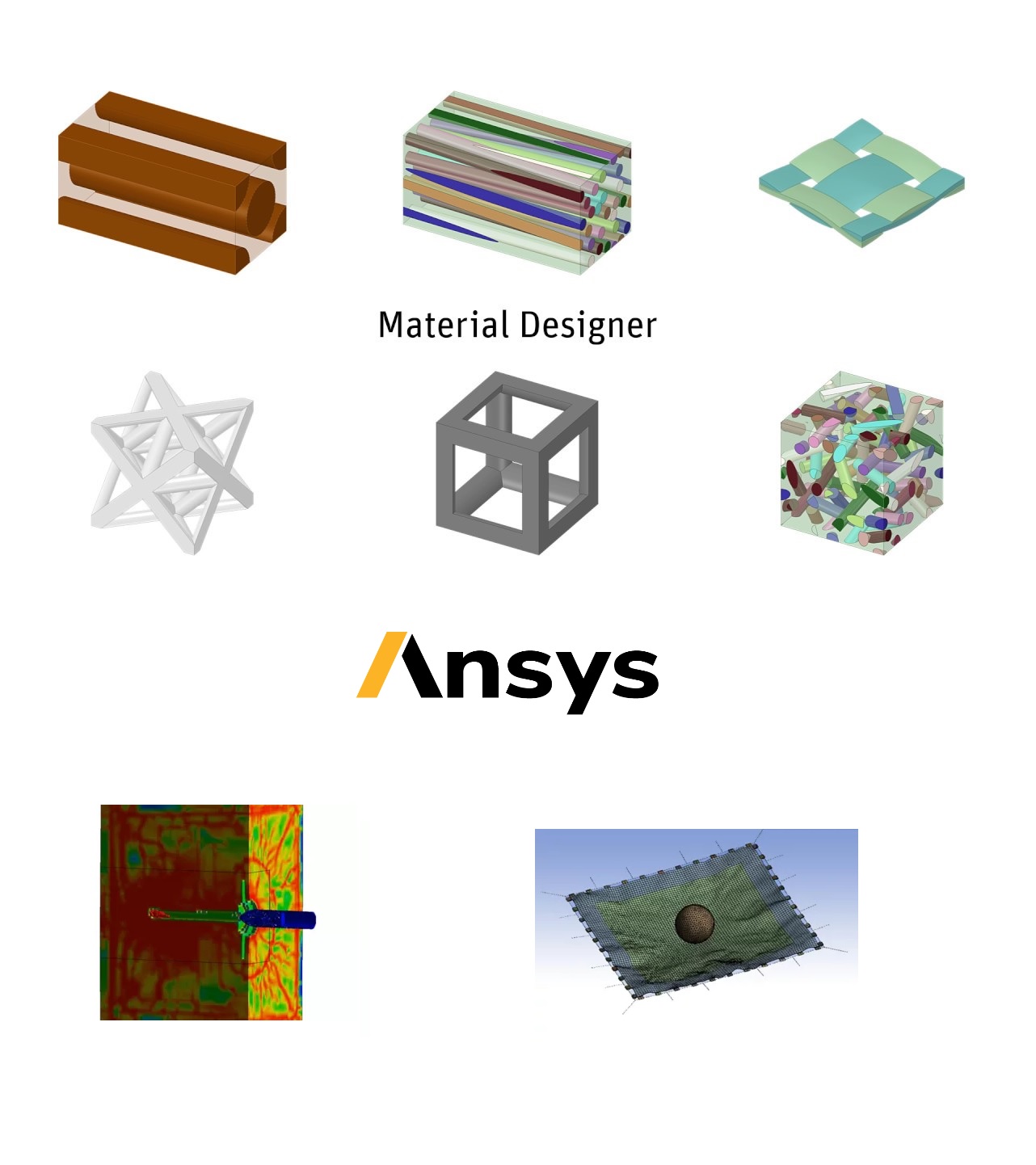
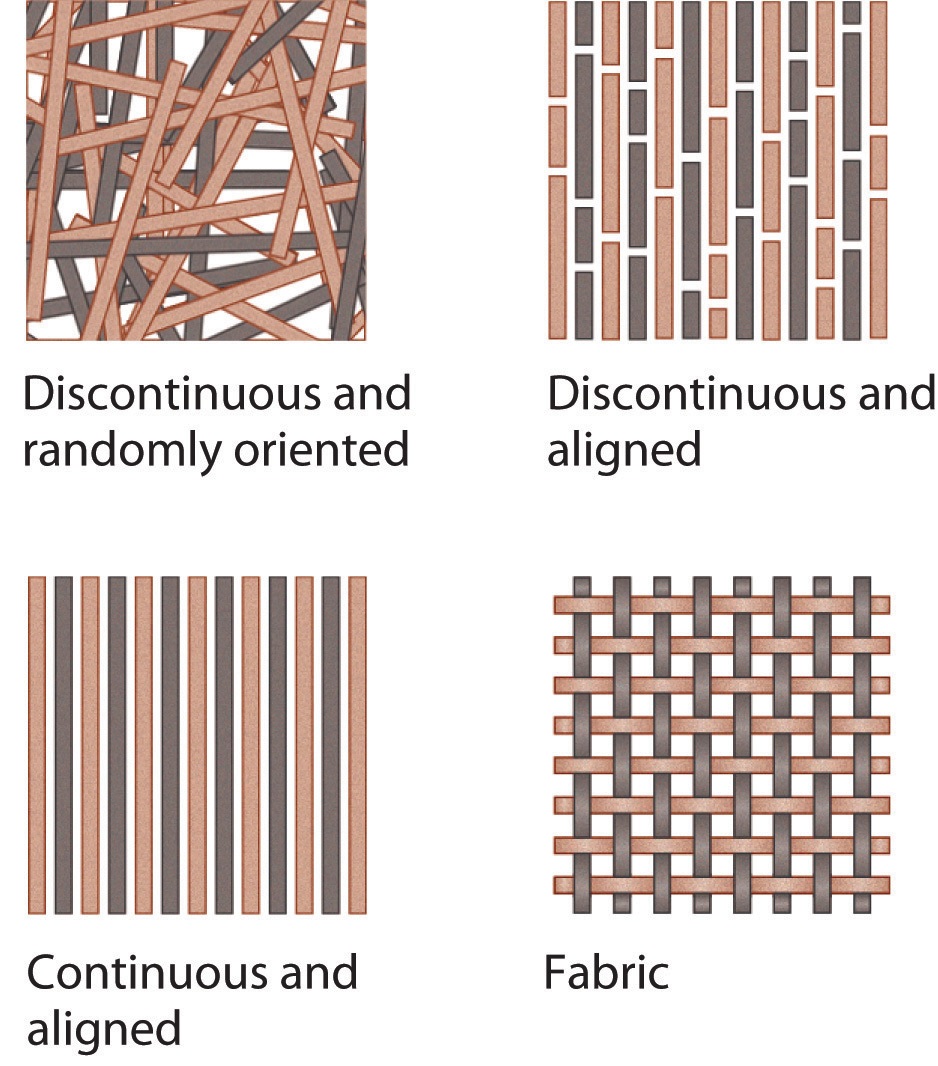
Unidirectional composites (UD) are a type of composite material that consist of fibers arranged in a single direction within a matrix material. These composites offer a wide range of options for tuning the material properties to meet specific performance requirements. They are commonly reinforced with different types of fibers, such as glass, carbon, or aramid, and can be made using both thermoset and thermoplastic matrices.
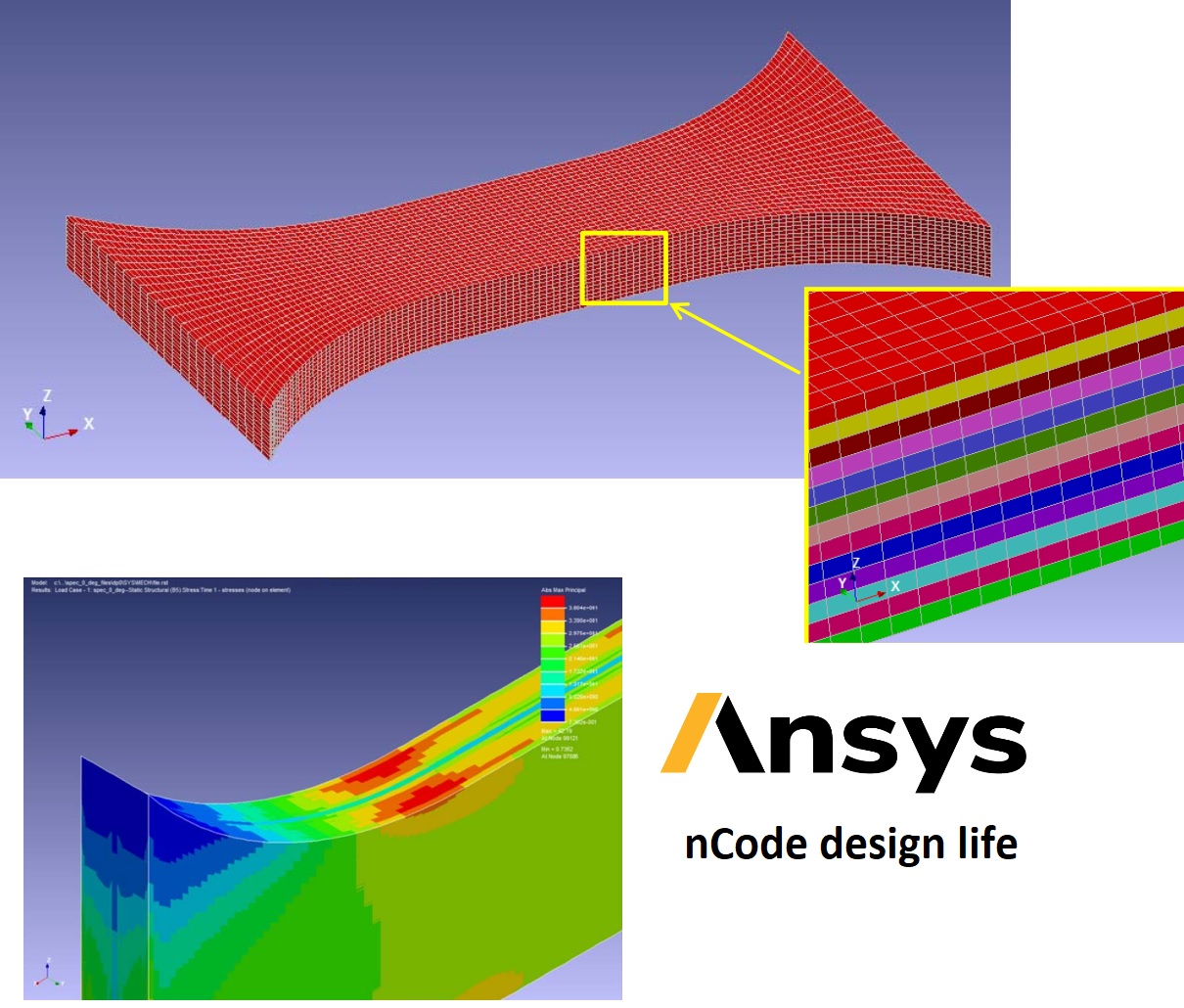
The fibers used in UD composites are typically straight and non-crimped, which allows for maximum efficiency in transferring load along the length of the fiber. The fibers are arranged in specific stacking sequences, with varying fiber volume fraction, ply thickness, and orientation, to achieve the highest possible in-plane laminate properties in the final composite component construction.
By varying the stacking sequence and fiber orientation, UD composites can be tailored to achieve specific mechanical properties, such as stiffness, strength, and toughness, in specific directions. This makes them ideal for applications that require high performance in certain directions, such as aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment.